Inverse Shade Trees for Non-Parametric Material Representation and Editing
ACM: ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2006.
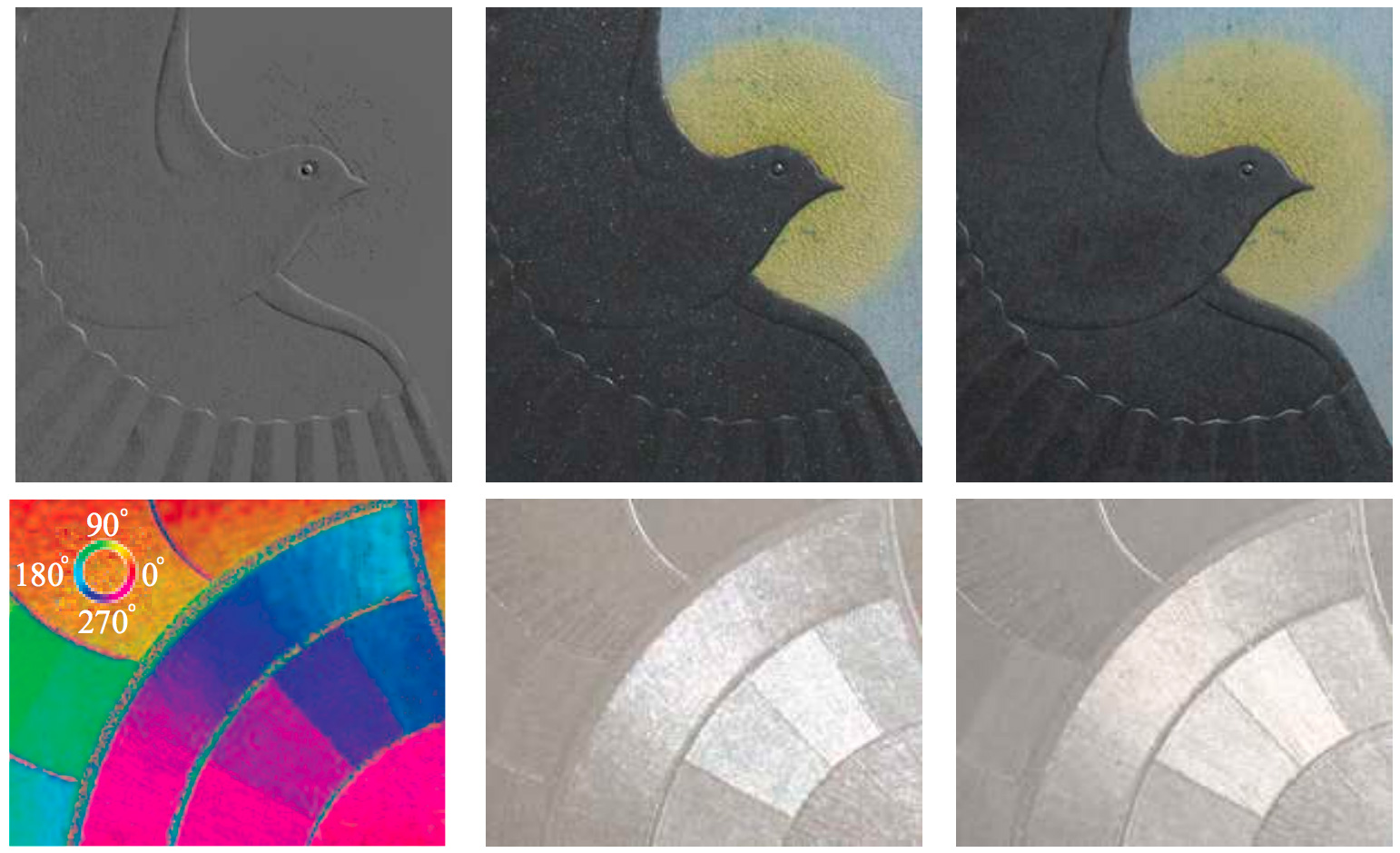
Recent progress in the measurement of surface reflectance has created a demand for non-parametric appearance representations that are accurate, compact, and easy to use for rendering. Another crucial goal, which has so far received little attention, is editability: for practical use, we must be able to change both the directional and spatial behavior of surface reflectance (e.g., making one material shinier, another more anisotropic, and changing the spatial “texture maps” indicating where each material appears). We introduce an Inverse Shade Tree framework that provides a general approach to estimating the “leaves” of a user-specified shade tree from high- dimensional measured datasets of appearance. These leaves are sampled 1- and 2-dimensional functions that capture both the directional behavior of individual materials and their spatial mixing patterns. In order to compute these shade trees automatically, we map the problem to matrix factorization and introduce a flexible new algorithm that allows for constraints such as non-negativity, sparsity, and energy conservation. Although we cannot infer every type of shade tree, we demonstrate the ability to reduce multi- gigabyte measured datasets of the Spatially-Varying Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (SVBRDF) into a compact rep- resentation that may be edited in real time.