Learning Vector Quantized Shape Code for Amodal Blastomere Instance Segmentation
arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.00985, 2020.
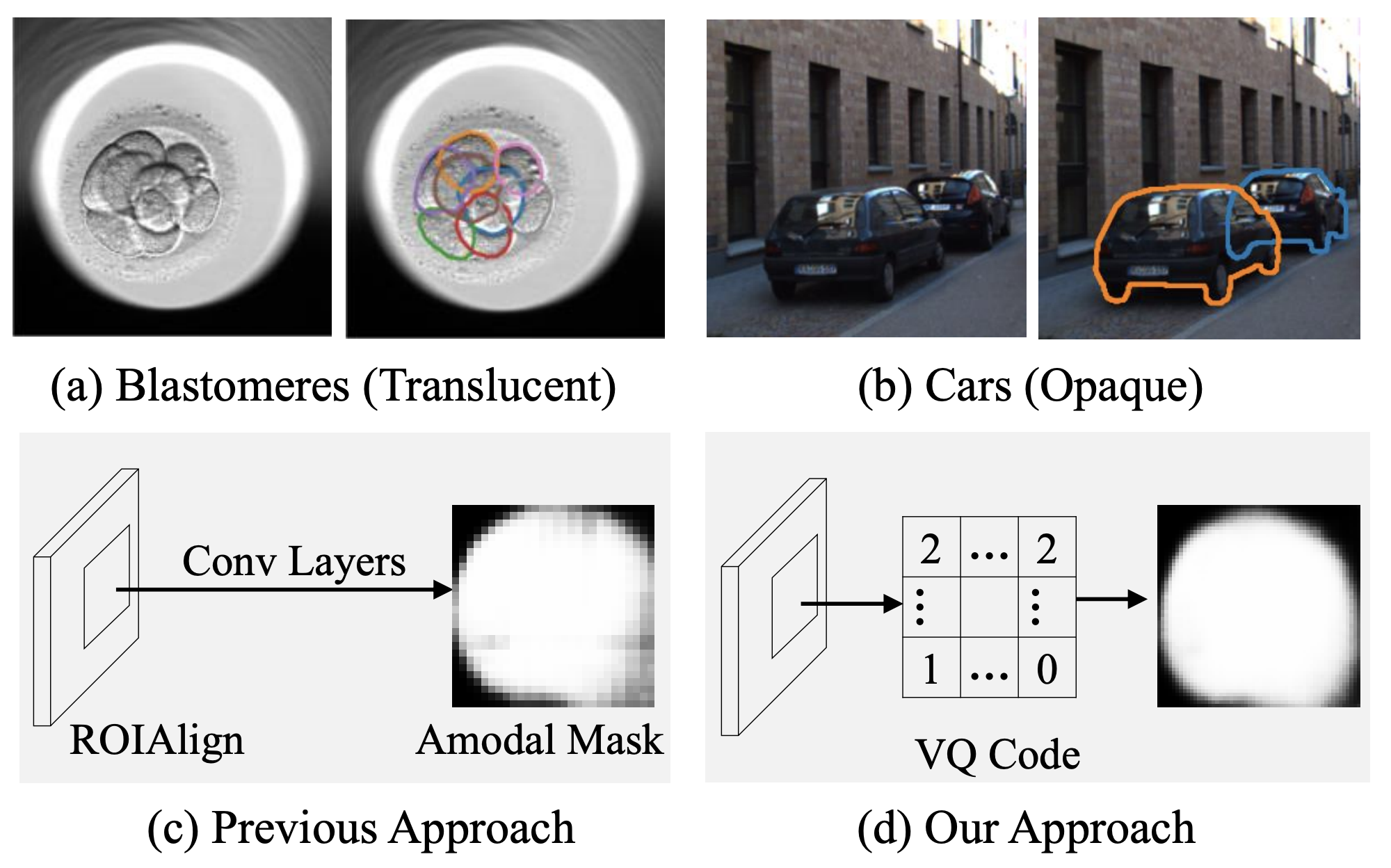
Blastomere instance segmentation is important for analyzing embryos' abnormality. To measure the accurate shapes and sizes of blastomeres, their amodal segmentation is necessary. Amodal instance segmentation aims to recover the complete silhouette of an object even when the object is not fully visible. For each detected object, previous methods directly regress the target mask from input features. However, images of an object under different amounts of occlusion should have the same amodal mask output, which makes it harder to train the regression model. To alleviate the problem, we propose to classify input features into intermediate shape codes and recover complete object shapes from them. First, we pre-train the Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE) model to learn these discrete shape codes from ground truth amodal masks. Then, we incorporate the VQ-VAE model into the amodal instance segmentation pipeline with an additional refinement module. We also detect an occlusion map to integrate occlusion information with a backbone feature. As such, our network faithfully detects bounding boxes of amodal objects. On an internal embryo cell image benchmark, the proposed method outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods. To show generalizability, we show segmentation results on the public KINS natural image benchmark. To examine the learned shape codes and model design choices, we perform ablation studies on a synthetic dataset of simple overlaid shapes. Our method would enable accurate measurement of blastomeres in in vitro fertilization (IVF) clinics, which potentially can increase IVF success rate.