Asymmetric 3D Context Fusion for Universal Lesion Detection
(MICCAI), 2021.
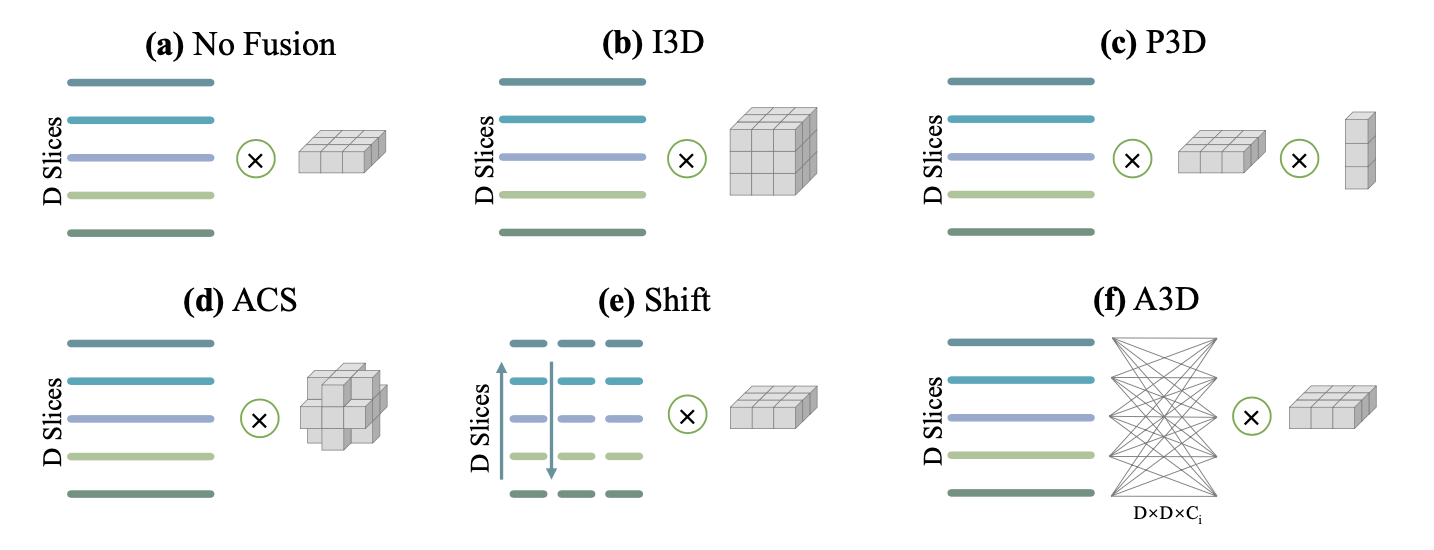
Modeling 3D context is essential for high-performance 3D medical image analysis. Although 2D networks benefit from large-scale 2D supervised pretraining, it is weak in capturing 3D context. 3D net- works are strong in 3D context yet lack supervised pretraining. As an emerging technique, 3D context fusion operator, which enables conver- sion from 2D pretrained networks, leverages the advantages of both and has achieved great success. Existing 3D context fusion operators are de- signed to be spatially symmetric, i.e., performing identical operations on each 2D slice like convolutions. However, these operators are not truly equivariant to translation, especially when only a few 3D slices are used as inputs. In this paper, we propose a novel asymmetric 3D context fu- sion operator (A3D), which uses different weights to fuse 3D context from different 2D slices. Notably, A3D is NOT translation-equivariant while it significantly outperforms existing symmetric context fusion op- erators without introducing large computational overhead. We validate the effectiveness of the proposed method by extensive experiments on DeepLesion benchmark, a large-scale public dataset for universal lesion detection from computed tomography (CT). The proposed A3D consis- tently outperforms symmetric context fusion operators by considerable margins, and establishes a new state of the art on DeepLesion. To fa- cilitate open research, our code and model in PyTorch is available at https://github.com/M3DV/AlignShift.